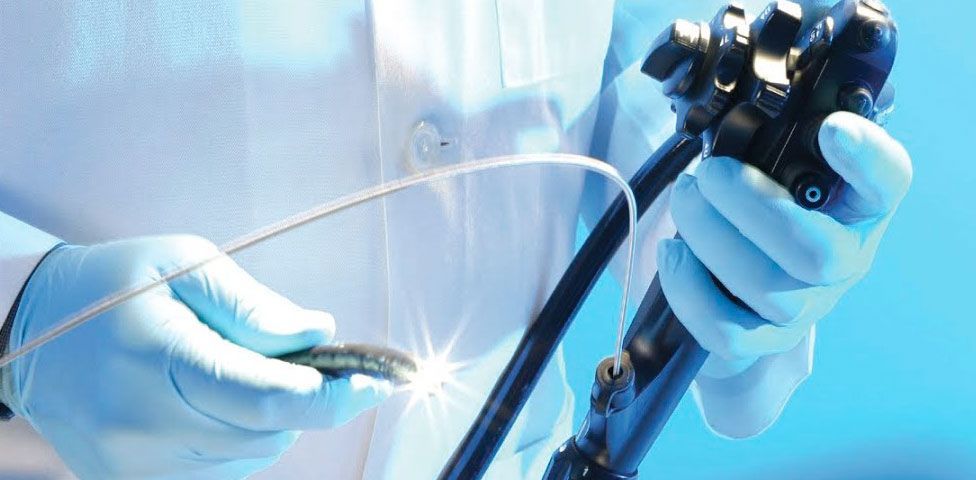
HOW ENDOSCOPY HELPS TO DETECT EARLY STAGE CANCER
But if you have an internal damage of the esophageal mucosa, gaster, and colon, it is not easy to identify the cause of your pain or symptoms. However, a simple and safe procedure known as endoscopy helps doctors to look into these hard-to-reach places in order to find out what is causing your pain and symptoms.
It is not surprising that endoscopy has become a real breakthrough in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. The endoscope allows to detect not only cancer, but also ulcers, polyps, and internal bleeding sites. Using endoscopy it is possible to take tissue samples (biopsy), enlarge narrowed areas, and stop bleeding. It is possible to remove polyps in the colon, thereby preventing the colon cancer.
Endoscopy is performed on an outpatient basis and is well tolerated by patients. But how to choose the best hospital for this procedure? We asked this question to endoscopists at the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy.

IT IS NO LONGER FGDS, IT IS VEGDS
Out of habit many people continue to call the procedure of "swallowing the tube" as fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). But modern endoscopes are no longer fiber endoscopes, they are video endoscopes, where an image is transmitted to the monitor screen using a small video camera. Therefore, it is more correct to call this procedure videoesophagogastroduodenoscopy or VEGDS (or alternatively VGDS).
“Very often we can hear such a question from patients: when will this unpleasant procedure be replaced with something more modern? Most probably, never. This is the most accurate, most reliable, most convenient way to diagnose early tumor diseases and inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases. In addition, new and more advanced equipment is appearing,” says the head of the Endoscopy Department of the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy.
The Endoscopy Department of the UMIT Center is equipped with an expert-class Pentax endoscopic unit from a Japanese manufacturer, one of the world leaders in the endoscopic equipment market. None private medical center in the capital is equipped with so powerful equipment with such high quality of transmitted images. It is quite expensive, the average cost of an endoscopy tower is 60-70 million Tenge. The endoscope has additional functions, for example, it is possible to stain the mucous membrane for clearer visualization.
In addition, modern endoscopes have a zoom function: the image on the screen is enlarged 3-4 times, it is possible to see even small capillaries. The shape and location of these capillaries helps to detect an initial stage of the malignant process.
MANY ARE CONCERNED WHETHER IT IS POSSIBLE TO GET AN INFECTION DURING ENDOSCOPY?
Endoscopy is an invasive examination, the device contacts with blood, mucus, biological fluids, which may contain pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Therefore, after each patient, endoscopic equipment must be carefully cleaned. There are special washing machines with fully automated processes of cleaning and disinfection of endoscopes.
The process of cleaning the endoscope in such a washing machine completely eliminates human intervention in the process. For example, imagine a situation where a nurse is in a hurry, fails to wait a prescribed time, and removes the endoscope from the disinfectant solution. But in the washing machine the door is hermetically sealed and will not open until the entire cycle is completed.
“We would recommend all patients to inquire if there is such a washing machine in any endoscopy unit where they plan to undergo an examination. All reusable instruments that are in close contact with blood and biofluids are processed in the same machine. It is very important,” recommends the specialists of the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy..

THIN TUBE, WIDE TUBE
We often hear from patients that they want to undergo an endoscopy procedure using only a thin tube. The head of the Endoscopic Department believes that this is not exactly correct. Each endoscope has its own task. Indeed, there are endoscopes of a smaller diameter - 6-7 mm, they are considered pediatric, intended for children. Standard endoscopes for examinations in adults vary in size from 9 to 9.9 mm.
“If so desired by the patient, thinner pediatric endoscopes can be used, a procedure is really easier to tolerate, but such endoscopes have a small forceps aperture (aperture through which doctors insert forceps and other instruments), not the entire set of instruments is available for such thin endoscopes. If, for example, during examination of a patient with such a thin endoscope, it is necessary to remove some formation with a knife, such a knife may not exist at all,” explains the head of the department.
In addition, a thin endoscope is very flexible, bends easily, and is difficult to pass to distant sites, such as the vertical branch of the duodenum, that is, it is impossible to perform a full-fledged procedure. In thin endoscopes, the material is taken with special forceps of small diameter, and the material may be less informative, since the pieces of material may be too small.
ENDOSCOPY UNDER SEDATION
“Endoscopy under sedation - it is very comfortable. Sedation helps both the patient to avoid stress and the doctor, who can safely perform the procedure. I am for sedation,” - the head of the Endoscopy Department expressed his opinion.
How is sedation performed? Anesthesiologist consults a patient, and if there are no contraindications, then the drug is administered.
“In fact, anesthesia is a medication sleep, the gag reflex is extinguished, patient is asleep. As soon as we complete the procedure, the drug supply is stopped and the patient wakes up and rests for a while. It is better to perform gastroscopy under anesthesia to have an opportunity to wash the gaster, slowly inspect every centimeter, use additional functions of magnification, staining,” - doctors say.
Sedation is not recommended during bronchoscopy, because endoscopist cannot give commands to patient, such as "breathe, bend or turn around." The cough reflex during anesthesia persists, patient coughs in the same way as if he is awake. This creates difficulties for a full diagnosis. Bronchoscopy is quite well tolerated without sedation.
WHAT IS MORE IMPORTANT IN ENDOSCOPY: GOOD EQUIPMENT OR EXPERIENCED DOCTOR?
“The main components of a successful endoscopy procedure are, first of all, good equipment, which is actually the eyes and hands of the endoscopist. The second point is, of course, the experience of a specialist. It is desirable that the endoscopist has a specialization in gastroenterology, understands surgery. Experience is required. Experience suggests where to focus attention, in which area there may be a malignant neoplasm, from which side it is better to take polyps, and so on,” explains the head of the Endoscopy Department.
ENDOSCOPY IN THE EARLY CANCER DIAGNOSIS
Esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer and breast cancer take leading positions in Kazakhstan. Endoscopy allows to examine the mucous membrane in detail, to see any even microscopic changes specific to cancerous and precancerous conditions. And what is the main, to take biopsy from abnormal sites. No other method allows to do this. Endoscopy is the gold standard in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer.
“In Kazakhstan, due to colorectal screening and oncology centers where polypectomy is performed, we practically do not see large and advanced formations in the colon. Over the last 6-7 years, we regularly remove polyps in the early stages. Any removed polyp from the colon is an investment in the future, in the health, and is the prevention of colon cancer development,” - notes the head of the Endoscopy Department of the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy.
HOW OFTEN IT IS NECESSARY TO UNDERGO ENDOSCOPIC EXAMINATIONS?
Endoscopists at the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy recommend: “Here in Kazakhstan, as part of colorectal screening, patients are first suggested to take a fecal occult blood test, and if blood is found in the feces, then a colonoscopy is performed at the second stage. But there is a nuance – in case of small polyps in the colon, about 2-5 mm in size, there will be no bleeding, but such polyp already exists and is visible. When blood appears in the feces, this is a signal that the formation in the intestine is already large, it breaks up and bleeds. Therefore, a colonoscopy after the age of 50 should be done every five years, regardless of whether you have any symptoms or not. And if there are symptoms such as bloat, false urges, blood in the feces, mucus in the feces, prolonged diarrhea, then colonoscopy should be performed from an earlier age”.
Doctors recommend to perform gastroscopy once every two years, starting from the age of 50 - if there are no symptoms. In case of disorders in the food passing, vomiting, heartburn, belching, abdominal pain, it is recommended to undergo gastroscopy much earlier. If there are erosive or ulcerative lesions, then gastroscopy should be performed during seasonal exacerbations once a year - either in autumn or in spring, when this exacerbation occurs.
WHAT IS COLONOSCOPY FOR?
Colonoscopy allows doctor to examine the colon mucosa for any changes. During colonoscopy, the doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube into patient's anus and slowly advances it into the rectum and colon. The colonoscope has its own lens and light source, allowing the doctor to view images on a video monitor. Typically, preparation for a colonoscopy consists of a restricted diet the day before the procedure and intake of a special cleansing solution or laxatives. For the procedure to be accurate and comprehensive, the colon must be completely clean, so it is obligatorily to follow the doctor's instructions.
Colonoscopy is well tolerated and rarely causes severe pain. During the procedure, patient may feel pressure, bloat, or spasms.
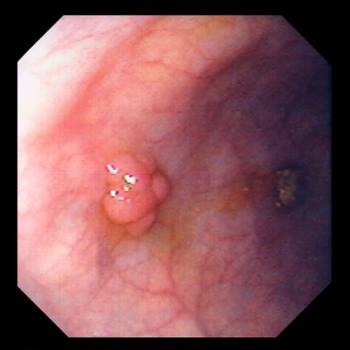
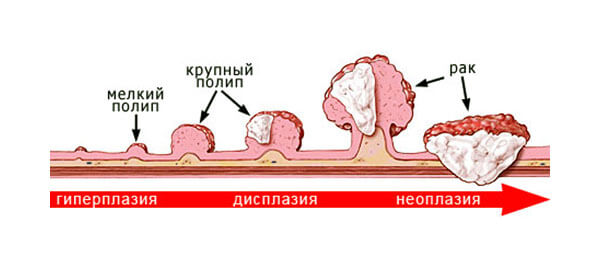
WHAT IS THE DANGER OF COLONIC POLYPS?
Polyps are abnormal growths in the colon mucosa that are usually benign. They vary in size from a tiny dot to several centimeters. Because cancer begins with polyps, removing them is an important way to prevent colorectal cancer.
“The whole point of screenings is to find any, even a very small formation. Don't worry when something is found. This will greatly reduce the risk of colon cancer in future. Most malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract grow from polyps,” - says the head of the Endoscopy Department.
The high-quality modern equipment, allows to find even the smallest neoplasms up to 5-7 mm in size and immediately, by examination without a biopsy, determine whether this process is benign or malignant. Polyps 5-7 mm in size are removed immediately upon first detection. From larger polyps biopsy is most often taken for histological examination. After the results of histology, such polyps are also removed. The larger the polyp, the more likely it is that malignant changes have already occurred there.
HOW IS BRONCHOSCOPY PERFORMED?
Bronchoscopy is the examination of the respiratory tracts using a bronchoscope. This is a rather complicated manipulation, the device is inserted through the larynx and vocal cords.
Before bronchoscopy, it is recommended to undergo a CT scan, the images show which part of the lung, which segment is affected, is it a peripheral or central formation. The bronchoscopy method allows to examine and take an analysis in the central formations. Peripheral tumors are not available for bronchoscopy.
The main purpose of bronchoscopy is to obtain material for histology to confirm the tumor process. Under the control of CT scans, the bronchoscope is directed purposefully into the segment where there is a formation.
WHY IS THE BIOPSY DONE?
“Biopsy is a powerful tool in the hands of a clinician. Only on the basis of histology it is possible to make a right diagnosis and prescribe an adequate and correct treatment. The sample is taken with the help of small sterile forceps from abnormal areas of the mucosa, from any formations, polyps, ulcer (a biopsy is not taken from erosions). A piece of tissue from 3 to 5 mm is torn off using forceps. The remaining defects of the mucosa, as a rule, do not bleed, these wounds heal quickly and without a trace. For example, using a microscopic examination of a piece of tissue, the presence of Helicobacter pylori, the cause of an ulcer, is determined,” - says the head of the Endoscopy Department.
HOW TO FIND A GOOD ENDOSCOPIST?
Previously, endoscopists were not specially trained; they were either surgeons, or gastroenterologists, or gynecologists. The breakthrough happened in the last 5-6 years. Even in small towns, modern endoscopy towers have appeared, but there is a lack of specialists.
“Today the Endoscopic Society has been created in Kazakhstan, we conduct master classes, seminars to train specialists on the basis of the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy. We want to popularize the specialty of an endoscopist, to talk about its importance and significance. We also want patients to know that with the help of a modern endoscope, a lot can be done in terms of the correct diagnosis of various diseases,” - sums up the head of the UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy.
The UMIT Oncological Center of Tomotherapy is located in the capital of Kazakhstan, Astana city, and offers a full range of medical services for the early diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The center has a team of the most experienced doctors and specialists: oncologists, mammologists, chemotherapists, radiologists, endoscopists, dermatologists, surgeons, medical physicists, etc. Patients are offered complete Check-Up programs for the diagnosis of the whole body.
For the treatment of oncological diseases, the center uses the most modern method of radiation therapy - tomotherapy. Radiation therapy is one of the main methods for cancer treatment. Thanks to new technological solutions, tomotherapy provides more accurate irradiation of the tumor and minimizes the radiation exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. This means that patients experience far fewer side effects.






 public offer
public offer